Case Report | DOI: https://doi.org/DSOMI-CA-25-012.
Aesthetic Rhinoplasty: Restoring Facial Symmetry and Patient Confidence Following Traumatic Nasal Deformity
Abstract
Rhinoplasty remains one of the most complex and nuanced surgical procedures in facial plastic surgery, characterized by its intricate challenges and long-term aesthetic considerations. This case report demonstrates the successful management of post-traumatic nasal asymmetry through a carefully planned open rhinoplasty approach. The surgical intervention not only addresses functional and aesthetic concerns but also highlights the critical importance of personalized surgical planning in facial reconstruction. The results of these cases show that minimally invasive intervention according to patient preference provides satisfactory aesthetic results for post-traumatic nasal deformities.
Introduction
Rhinoplasty has undergone significant transformation over the past decades, evolving from a standardized reduction procedure to a highly personalized, problem-oriented intervention [1,2]. Contemporary approaches emphasize tissue preservation, structural modification, and individualized aesthetic goals [3,4]. Traumatic nasal deformities present unique challenges, often requiring comprehensive assessment of both functional and aesthetic components [5]
Case Report
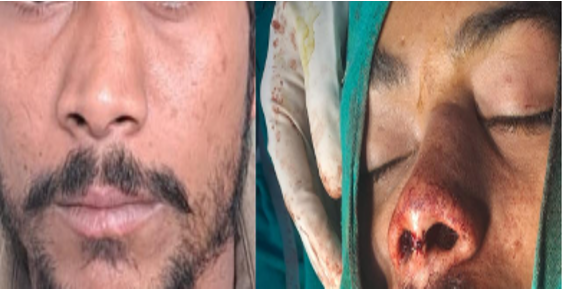
A 24-year-old male presented at Jaya Maxwell Hospital with a complex post-traumatic nasal deformity resulting from previous facial fractures. The patient reported significant nasal asymmetry and aesthetic concerns approximately 2.5 years following his initial trauma. (Figure I)

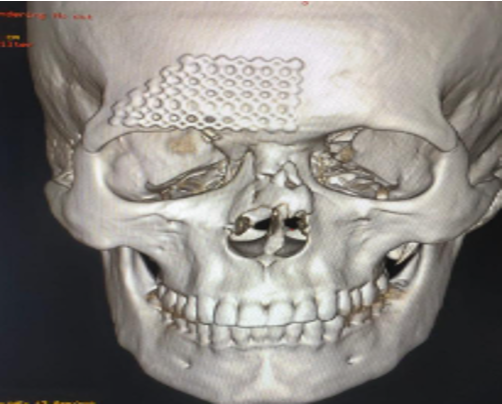
Clinical Findings: Comprehensive 3D CT facial imaging revealed the following findings (figure II):
- Evidence of old bilateral nasal fracture
- Excessive bone formation on the left nasal side
- Bone loss on the right nasal side
- Consequent nasal deviation towards the left
- Residual forehead mesh from previous reconstruction
Surgical Planning: The proposed surgical strategy involved, open rhinoplasty approach followed by reduction of excessive left-sided bone calcification and subsequent restoration of nasal symmetry.
Surgical Technique: An open rhinoplasty technique was employed, characterized by a columellar incision between nostrils after which careful soft tissue flap elevation was done till the bone was visible and palpable. Precise bone filing to achieve symmetry. Immediate intraoperative photograph was taken after the procedure. (Figure III)
Surgical Closure and Postoperative Management: The reduction procedure was meticulously completed with precise soft tissue reconstruction. Layered closure was done wherein the cartilages were sutured first using 3-0 vicryl in vertical mattress pattern, followed by skin approximation using 5-0 prolene sutures in simple interrupted pattern. Postoperative immobilisation was done using a nasal splint applied for 14 days. Systemic steroids and prophylactic antibiotics were prescribed for 7 days postoperatively.
Outcome: The procedure successfully addressed the patient's aesthetic concerns, demonstrating the potential of targeted surgical intervention in managing post-traumatic facial deformities.
Recognizing the profound psychological impact of facial reconstruction, dedicated counselling sessions were implemented to address the patient's emotional concerns and support his psychological adaptation to the surgical outcome.
Discussion
Rhinoplasty represents a complex intersection of surgical precision, aesthetic vision, and patient-specific considerations. [1-4] Each procedure demands a nuanced approach, where technical expertise must be harmoniously balanced with individual anatomical variations and patient expectations. The surgical management of post-traumatic nasal deformity, requires a comprehensive, individualized approach that addresses both aesthetic and functional concerns. Careful preoperative evaluation, combined with the appropriate choice of open or closed rhinoplasty, allows for tailored correction of bony and cartilaginous deformities. Key surgical techniques include precise osteotomies, septoplasty with structural grafting, cartilage grafting for support and contour, and specialized maneuvers for tip and dorsal corrections. Functional restoration through airway management is emphasized alongside aesthetic refinement. [5]
Key Surgical Considerations:
- Patient-specific challenges: Excessive aesthetic concerns
- Surgical limitations: Patient's reluctance towards comprehensive grafting
- Aesthetic compromise: Satisfactory result achieved, though potential for further optimization existed
This case exemplifies the delicate balance between surgical recommendations and patient autonomy. While ideal surgical outcomes often require comprehensive interventions, patient consent and comfort remain paramount. [6,7]
Limitations and Future Perspectives:
- The decision to forgo grafting potentially limited optimal aesthetic reconstruction
- Long-term follow-up essential to assess structural stability and aesthetic evolution
- Patient counselling crucial in managing expectations and psychological adaptation
Conclusion
Successful rhinoplasty transcends mere surgical technique. Meticulous planning, execution, and postoperative care are critical to achieving optimal, lasting outcomes in patients with post-traumatic nasal deformities. It represents a holistic approach to patient care, integrating surgical expertise, aesthetic sensitivity, and psychological support. By addressing both physical reconstruction and patient confidence, we transform not just appearance, but quality of life.
References
-
Guyuron B. (2015), Innovations in Aesthetic Rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 136(4):675-682.
View at Publisher | View at Google Scholar -
Daniel RK. (2016), Rhinoplasty: Aesthetic and Functional Analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 40(3):368-382.
View at Publisher | View at Google Scholar -
Rohrich RJ, et al. (2014) Management of Complex Nasal Deformities. Plast Reconstr Surg. 134(6):1276-1286.
View at Publisher | View at Google Scholar -
Toriumi DM. (2018) Modern Rhinoplasty: Achieving Optimal Aesthetic Outcomes. Facial Plast Surg. 34(5):453-464.
View at Publisher | View at Google Scholar -
Berrezouk, M. , Kamal, F. , Maidam, S. , Lakouichmi, M. and Abouchadi, A. (2024) Principles and Techniques of Post-Traumatic Rhinoplasty: A Review of the Literature. Modern Plastic Surgery, 14, 74-86.
View at Publisher | View at Google Scholar -
Most SP. (2016) Patient-Centered Decision Making in Rhinoplasty. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 18(3):197-204.
View at Publisher | View at Google Scholar -
Papel ID. (2019) Psychological Considerations in Facial Plastic Surgery. Facial Plast Reconstr Surg. 35(4):312-320.
View at Publisher | View at Google Scholar






